
- February 2, 2026
- Tejhaksh
- 0 Comments
- Database, Microsoft, Uncategorized
What is Microsoft SQL Server? Features, History, Uses & Versions Explained
Introduction to SQL Server
In today’s data-driven world, efficiently managing, storing, and analyzing data has become essential for businesses of every size. This is where Microsoft SQL Server plays a crucial role. Developed by Microsoft, SQL Server is one of the most widely used and powerful relational database management systems (RDBMS) in the world, trusted by organizations across industries.
Whether you are a beginner looking to understand what SQL Server is, a developer exploring reliable database platforms, or a business owner searching for a secure and scalable data solution, this guide is designed for you. In this article, we will explain the meaning of SQL Server, its history, key features, uses, versions, database services, and also provide a comparison with MySQL, giving you a complete and clear overview.
What Is Microsoft SQL Server?
Microsoft SQL Server, commonly known as SQL Server, is a relational database management system (RDBMS) developed by Microsoft for storing and managing data efficiently. It stores and manages data using Structured Query Language (SQL), allowing users to create, read, update, and delete data efficiently while ensuring high security, reliability, and performance.
In simple terms, SQL Server is used to store large amounts of data in an organized way and retrieve it quickly whenever needed.
It is an enterprise-grade database platform that supports:
- Data storage and processing
- Business intelligence and analytics
- Web applications, ERP, CRM, and e-commerce systems
- Banking and financial applications
Microsoft SQL Server also works seamlessly with other Microsoft products like Windows Server, Azure, Power BI, .NET, and Visual Studio, making it a preferred choice for businesses and enterprises.
History of Microsoft SQL Server
The evolution of Microsoft SQL Server highlights its transformation from a basic database system into a powerful, enterprise-grade data platform. Here’s a timeline of its major milestones:
- 1989 – The first version of SQL Server was launched in collaboration with Sybase and Ashton-Tate.
- 1993 – Microsoft split from Sybase and began developing SQL Server independently.
- 1995 – SQL Server 6.0 was released, bringing significant performance improvements.
- 2000–2008 – Enterprise-level features like advanced indexing, reporting, and analytics were introduced, making SQL Server suitable for large-scale business applications.
- 2012 onwards – The focus shifted to cloud integration, big data, AI capabilities, and enhanced security.
- Latest versions – SQL Server now offers deep integration with Microsoft Azure, AI-powered analytics, and robust support for modern data workloads.
From its early beginnings, SQL Server has evolved into a comprehensive data platform, enabling organizations to manage, analyze, and secure data efficiently.
Uses of SQL Server and Who Uses It
Microsoft SQL Server is a versatile relational database platform used to store, manage, and analyze data efficiently. It serves organizations of all sizes, from small websites to large enterprises, providing secure, scalable, and high-performance data management.
Key Uses of SQL Server:
- Storing structured data securely
- Managing large databases
- Running complex queries
- Data analysis and reporting
- Supporting high-traffic applications
- Powering business intelligence (BI) solutions
Who Uses SQL Server:
- Software developers building applications
- Data analysts and data scientists working on insights
- Banks and financial institutions requiring secure transactions
- Government organizations managing large datasets
- Healthcare systems handling patient records
- E-commerce companies supporting online platforms
- Educational institutions storing academic data
In short, any organization that requires reliable, fast, and secure data management can benefit from SQL Server.
Key Features of Microsoft SQL Server
One of the main reasons behind Microsoft SQL Server’s popularity is its comprehensive and powerful set of features. These features make it a preferred choice for enterprises, developers, and data professionals alike.
1. High Security
SQL Server ensures that your data is always protected and secure through:
- Data Encryption: Safeguards sensitive data when stored in the database and while being transmitted.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Grants permissions based on user roles, ensuring only authorized access.
- Advanced Authentication: Supports multi-factor authentication and integration with Windows Active Directory for enhanced security.
2. High Performance
SQL Server is optimized for fast and efficient data processing:
- Optimized Query Processing: Uses intelligent query optimization for faster results.
- In-Memory Technology: Improves performance for transactional and analytical workloads.
- Advanced Indexing: Supports clustered, non-clustered, and full-text indexes to speed up data retrieval.
- Optimized query processing: uses intelligent Query optimization for faster results
3. Scalability
SQL Server can handle databases of all sizes, from small applications to enterprise-level systems:
- Supports millions of records and concurrent users efficiently.
- Handles enterprise-grade workloads without compromising performance.
4. Business Intelligence (BI)
SQL Server offers a rich BI ecosystem to transform raw data into actionable insights:
- Integration with Power BI: Easily connect and visualize data.
- Advanced Analytics & Reporting: Built-in reporting services, data mining, and analytics for informed decision-making.
5. Backup and Recovery
Data safety is critical, and SQL Server provides robust backup and recovery options:
- Automated Backups: Schedule backups to ensure data is always protected.
- Disaster Recovery Solutions: High availability features like Always On Availability Groups for uninterrupted operations.
6. Cloud Integration
SQL Server works seamlessly with the cloud, enabling modern hybrid and cloud-based solutions:
- Microsoft Azure Integration: Easily deploy databases to the cloud.
- Cloud-Based Analytics and Storage: Leverage cloud power for big data, AI, and advanced analytics.
7. Additional Features
- Advanced Data Types: Supports XML, JSON, spatial, and graph data types for diverse applications.
- Transaction Management: Ensures data integrity with ACID-compliant transactions.
- Developer Tools: Tight integration with Visual Studio and .NET for building applications efficiently.
- Monitoring and Performance Tools: SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and other monitoring tools help maintain database health.
In short, SQL Server combines security, performance, scalability, and advanced analytics in a single platform, making it ideal for modern enterprise data management.
Database Services Provided by Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is not just a database—it is a complete data platform offering a wide range of services to manage, process, analyze, and visualize data. Its comprehensive suite of services makes it suitable for enterprise-level applications and modern data solutions.
1. Database Engine Services
The core service of SQL Server, the Database Engine handles:
- Data storage and retrieval
- Transaction management
- Query processing and optimization
It ensures high performance, reliability, and data integrity for all applications.
2. SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)
SSIS is designed for data integration and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) operations:
- Integrates data from multiple sources
- Cleanses and transforms data for analytics
- Automates complex data workflows for enterprise applications
3. SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS)
SSAS provides advanced data analysis and business intelligence capabilities:
- Supports OLAP (Online Analytical Processing) for analyzing multidimensional data efficiently.
- Enables data mining and predictive analytics
- Helps organizations derive insights from large datasets
4. SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS)
SSRS is a powerful reporting and data visualization tool:
- Creates interactive, paginated, and mobile-friendly reports
- Integrates with dashboards and BI tools
- Provides real-time reporting for better decision-making
5. SQL Server Machine Learning Services
SQL Server supports AI and machine learning directly within the database:
- Integrates with R and Python for advanced analytics
- Allows predictive modeling on large datasets
- Enables smarter data-driven decisions without moving data externally
With these services, SQL Server goes beyond being just a relational database. It becomes a comprehensive platform for data management, business intelligence, analytics, and AI-driven solutions, making it a preferred choice for modern enterprises.
SQL Server Versions and Their Evolution
Microsoft SQL Server has evolved significantly since its inception, with each version introducing new features, improved performance, enhanced security, and advanced analytics capabilities. Here’s a simplified overview of its major versions:
- SQL Server 2000 – Introduced basic enterprise-level database features and improved T-SQL capabilities.
- SQL Server 2005 – Added integration services, reporting services, and enhanced security features.
- SQL Server 2008 / 2008 R2 – Focused on performance improvements, backup enhancements, and spatial data support.
- SQL Server 2012 – Introduced Always On Availability Groups for high availability and disaster recovery, plus better BI support.
- SQL Server 2014 – Brought in-memory OLTP technology and performance enhancements for large-scale databases.
- SQL Server 2016 – Focused on advanced security features, real-time operational analytics, and seamless cloud integration.
- SQL Server 2017 – Introduced cross-platform support, enabling SQL Server to run on Linux and Docker containers.
- SQL Server 2019 – Enhanced big data clusters, intelligent query processing, and data virtualization.
- SQL Server 2022 – The latest major release, offering tight integration with Microsoft Azure, advanced security, and AI-powered analytics.
Each version reflects Microsoft’s commitment to innovation, ensuring SQL Server remains a robust, secure, and high-performance platform for modern data management and analytics.
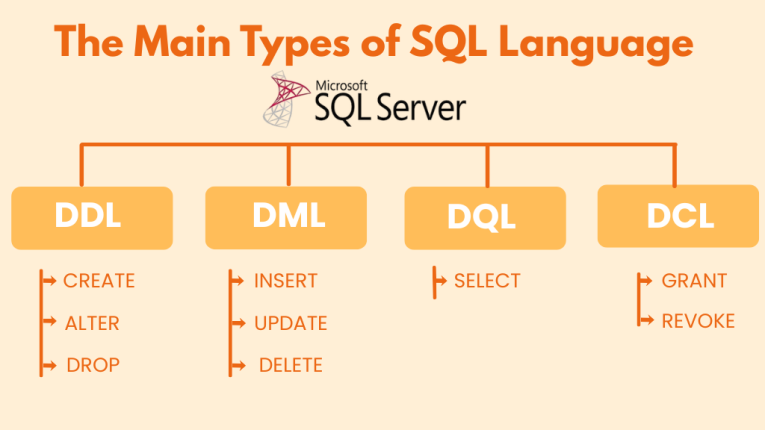
The Main Types of SQL Language
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language used to interact with relational databases like Microsoft SQL Server. It is divided into four main categories, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands are used to define, modify, and remove database structures such as tables, indexes, and schemas.
Common DDL commands:
- CREATE – Create new databases or tables
- ALTER – Modify existing database structures
- DROP – Delete databases or tables
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands are used to manipulate and manage data within tables.
Common DML commands:
- INSERT – Add new records to a table
- UPDATE – Modify existing records
- DELETE – Remove records from a table
3. Data Query Language (DQL)
DQL commands are used to retrieve data from the database.
Common DQL command:
- SELECT – Fetch data based on specific criteria
4. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL commands manage user permissions and access control in the database.
Common DCL commands:
- GRANT – Give permissions to users or roles
- REVOKE – Remove permissions
Together, these four categories form the foundation of SQL Server operations, enabling database creation, data management, querying, and secure access control.
SQL Server vs MySQL: Key Differences
Microsoft SQL Server and MySQL are both popular relational database management systems, but they serve different purposes and audiences. Here’s how they compare:
Developer:
- SQL Server: Developed by Microsoft
- MySQL: Developed by Oracle
Best For:
- SQL Server: Ideal for enterprise-level applications and large organizations
- MySQL: Popular for web applications, startups, and open-source projects
Security:
- SQL Server: Offers very high security, including advanced authentication, encryption, and role-based access control
- MySQL: Provides moderate security, suitable for smaller applications
Cost:
- SQL Server: Paid editions with some free versions (like Express Edition)
- MySQL: Mostly free and open-source with optional commercial support
Operating System Support:
- SQL Server: Runs on Windows and Linux
- MySQL: Fully cross-platform, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, and others
Advantages of Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server offers a wide range of benefits, making it a preferred choice for enterprises, developers, and data professionals. Key advantages include:
- User-Friendly and Easy to Learn: SQL Server has an intuitive interface and well-structured query language (T-SQL), making it easy for beginners and experienced developers to work with databases efficiently.
- Strong Community and Documentation: With a large global user base and extensive official documentation, SQL Server provides ample support, tutorials, and best practices for troubleshooting and learning.
- Regular Updates and Enterprise Support: Microsoft continuously releases updates, security patches, and feature enhancements, ensuring the platform remains secure, stable, and up-to-date.
- Cloud-Ready Architecture: SQL Server integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Azure, enabling hybrid cloud solutions, cloud storage, and cloud-based analytics for modern enterprise needs.
- Advanced Analytics and AI Capabilities: SQL Server supports big data, AI, and machine learning integration, allowing organizations to analyze large datasets, run predictive models, and gain actionable insights without moving data externally.
- High Security and Reliability: Built-in encryption, access control, and disaster recovery features ensure data is protected and available, even for mission-critical enterprise applications.
Microsoft SQL Server combines ease of use, advanced functionality, and enterprise-grade reliability, making it a top choice for modern data management and analytics.
Future of Microsoft SQL Server
The future of Microsoft SQL Server is strongly aligned with advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data technologies. Microsoft continues to enhance SQL Server to meet the demands of modern, data-driven organizations.
With deep integration into Microsoft Azure, SQL Server supports hybrid and cloud-native environments, allowing businesses to scale seamlessly while maintaining high performance and security. Built-in machine learning and AI capabilities enable smarter data analysis, predictive insights, and automation directly within the database.
In addition, SQL Server’s focus on advanced analytics, intelligent query processing, and enhanced security ensures it remains a reliable platform for enterprise workloads. As organizations increasingly rely on real-time data and cloud solutions, SQL Server is well-positioned to remain a future-ready, intelligent data platform for years to come.
Conclusion
Microsoft SQL Server is more than just a database—it is a complete data management and analytics platform. From understanding what is SQL Server, exploring its history, features, uses, versions, to comparing it with MySQL, we can confidently say that SQL Server remains one of the most powerful and reliable database systems in the world.
Whether you are a beginner, developer, or enterprise user, learning and using SQL Server can open doors to high-demand career opportunities and scalable business solutions.




Leave a Comment